Anatolia, a land of ancient wonders and enduring legacy, stands as a testament to the rich tapestry of human history. From the dawn of civilization to the modern era, this captivating region has played a pivotal role in shaping the course of humanity, leaving an indelible mark on the world stage.
Nestled at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, Anatolia’s strategic location has made it a melting pot of cultures, a vibrant hub where East meets West. Throughout the ages, it has witnessed the rise and fall of mighty empires, the birth of groundbreaking ideas, and the flourishing of diverse artistic traditions.
Anatolia: A Historical Perspective
Anatolia, the peninsula forming the westernmost part of Asia, has been a cradle of civilization for millennia. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has made it a melting pot of cultures and a stage for some of history’s most pivotal events.
Timeline of Key Events
- 10,000 BCE: Arrival of the first settlers, the Neolithic farmers.
- 7000 BCE: Emergence of the Çatalhöyük civilization, one of the earliest known urban settlements.
- 3000 BCE: Development of the Bronze Age in Anatolia.
- 2000 BCE: Arrival of the Hittites, an Indo-European people who established a powerful empire.
- 1200 BCE: Collapse of the Hittite Empire and the rise of the Phrygians.
- 546 BCE: Conquest of Anatolia by the Persian Empire.
- 334 BCE: Alexander the Great invades Anatolia.
- 1st century CE: Anatolia becomes a province of the Roman Empire.
- 1071 CE: Battle of Manzikert, marking the beginning of Turkish rule in Anatolia.
- 1299 CE: Foundation of the Ottoman Empire in Anatolia.
- 1923 CE: Establishment of the Republic of Turkey.
Major Civilizations
- Çatalhöyük (7000-5700 BCE): One of the earliest known urban settlements, with a population of over 10,000 people.
- Hittite Empire (2000-1200 BCE): A powerful Indo-European empire that ruled over much of Anatolia.
- Phrygian Kingdom (1200-700 BCE): A Phrygian kingdom that flourished in central Anatolia.
- Lydian Kingdom (700-546 BCE): A Lydian kingdom that was known for its wealth and trade.
- Persian Empire (546-334 BCE): The Persian Empire conquered Anatolia and ruled it for over two centuries.
- Hellenistic Period (334-1st century BCE): After the conquest of Alexander the Great, Anatolia became part of the Hellenistic world.
- Roman Empire (1st century BCE-395 CE): Anatolia became a province of the Roman Empire and was known as Asia Minor.
- Byzantine Empire (395-1453 CE): The Byzantine Empire, the eastern half of the Roman Empire, ruled over Anatolia for over a millennium.
- Ottoman Empire (1299-1923 CE): The Ottoman Empire, a powerful Islamic empire, ruled over Anatolia for over six centuries.
- Republic of Turkey (1923-present): The Republic of Turkey was founded in 1923 after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire.
Geography and Climate of Anatolia
Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula located in western Asia. It is bordered by the Black Sea to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. Anatolia is a region of great geographical diversity, with a complex geological history that has shaped its unique landscape.
Geographical Features
- Mountains: Anatolia is home to several mountain ranges, including the Pontic Mountains along the Black Sea coast, the Taurus Mountains in the south, and the Anti-Taurus Mountains in the central region.
- Plateaus: Anatolia is characterized by several high plateaus, including the Anatolian Plateau in the central region and the Armenian Plateau in the east.
- Rivers: The major rivers of Anatolia include the Kizilirmak, the Sakarya, and the Tigris.
- Lakes: Anatolia is home to several large lakes, including Lake Van, Lake Tuz, and Lake Beyşehir.
Climate
Anatolia has a diverse climate, with a range of conditions from the humid subtropical climate along the Black Sea coast to the arid climate in the central plateau. The region experiences hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters.
Anatolia, a region steeped in ancient history and cultural heritage, offers a glimpse into the past. From its bustling cities to its tranquil countryside, Anatolia’s allure extends beyond its borders. Just like the picturesque town of Annecy, France , nestled amidst the French Alps, Anatolia enchants with its unique blend of nature and history, inviting travelers to discover its timeless treasures.
The climate of Anatolia has a significant impact on the region’s agriculture and economy. The fertile soils and abundant water resources of the coastal regions support a thriving agricultural sector, while the arid climate of the central plateau limits agricultural production.
Map of Anatolia
[Insert map of Anatolia highlighting its major geographical features here]
Anatolia’s Cultural Heritage
Anatolia, a region in western Asia, boasts a rich and diverse cultural heritage that spans thousands of years. Throughout history, Anatolia has been a melting pot of civilizations, each leaving its mark on the region’s culture, art, music, and literature.
Cultural Influences
The cultural heritage of Anatolia has been shaped by various influences, including:
- Ancient Anatolian Civilizations: The Hittites, Phrygians, Lydians, and others established flourishing civilizations in Anatolia, contributing to its cultural foundations.
- Hellenic Influence: Anatolia came under the influence of Greek culture during the Hellenistic period, which left a lasting impact on its art, architecture, and philosophy.
- Roman Empire: As part of the Roman Empire, Anatolia absorbed Roman influences in law, administration, and infrastructure.
- Byzantine Empire: The Byzantine Empire, centered in Constantinople, had a profound impact on Anatolia’s cultural and religious landscape, introducing Christianity and fostering the development of Byzantine art and architecture.
- Islamic Influence: With the arrival of the Seljuk Turks in the 11th century, Anatolia began to experience Islamic influence, which shaped its architecture, literature, and music.
Art
Anatolian art is renowned for its intricate designs, vibrant colors, and diverse forms. Examples include:
- Hittite Rock Reliefs: Carved into rock faces, these reliefs depict scenes of war, hunting, and religious rituals.
- Byzantine Mosaics: Found in churches and palaces, these mosaics showcase religious themes and depict historical events.
- Seljuk Architecture: Characterized by pointed arches, domes, and elaborate tilework, Seljuk architecture can be seen in mosques, palaces, and caravanserais.
Music
Anatolian music is a rich tapestry of traditional and contemporary sounds. Some notable genres include:
- Folk Music: Rooted in ancient Anatolian traditions, folk music is characterized by its use of bağlama (a stringed instrument) and rhythmic patterns.
- Sufi Music: Associated with Islamic mysticism, Sufi music is known for its spiritual lyrics and trance-inducing melodies.
- Modern Turkish Music: A fusion of traditional and Western influences, modern Turkish music encompasses a wide range of styles, from pop and rock to classical.
Literature
Anatolian literature has a long and distinguished history, with works that reflect the region’s cultural diversity.
- Epic of Gilgamesh: An ancient Mesopotamian epic, part of which was found in Anatolia, it tells the story of a legendary king and his quest for immortality.
- Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey: These epic poems, traditionally attributed to the Greek poet Homer, are believed to have been influenced by Anatolian mythology.
- Mevlana Rumi: A 13th-century Persian poet and mystic who lived in Anatolia, Rumi is known for his mystical poetry and teachings on love and unity.
Anatolia’s Economic Importance
Anatolia has been a crucial economic hub throughout history, boasting abundant natural resources and a strategic location connecting Europe and Asia. Its economic significance has been recognized for centuries, contributing to the prosperity of empires and civilizations.
The region is rich in minerals, including copper, iron, lead, and zinc, which have fueled industrial development and trade. Anatolia’s fertile plains and favorable climate have also made it an agricultural powerhouse, producing a wide range of crops, including wheat, barley, cotton, and olives.
Anatolia, with its rich history and breathtaking landscapes, has captured the hearts of travelers for centuries. If you seek top luxury travel destinations, consider venturing beyond its borders to experience the world’s finest offerings. From opulent palaces to pristine beaches, the top luxury travel destinations await your exploration.
Yet, Anatolia remains an enchanting gem, its ancient ruins and vibrant culture beckoning you to return.
Industries and Resources
- Agriculture: Anatolia’s fertile soil and temperate climate have made it a major agricultural region, producing a wide range of crops such as wheat, barley, cotton, and olives.
- Mining: Anatolia is rich in mineral resources, including copper, iron, lead, and zinc, which have been mined and exported for centuries.
- Tourism: Anatolia is home to numerous historical and cultural sites, including ancient ruins, mosques, and churches, which attract tourists from around the world.
- Manufacturing: Anatolia has a growing manufacturing sector, producing a wide range of goods, including textiles, food products, and machinery.
Economic Output and Trade
Anatolia’s economic output is significant, contributing to Turkey’s overall economic growth. The region is a major exporter of agricultural products, minerals, and manufactured goods. It is also a key destination for foreign investment and tourism.
| Year | GDP (USD billions) | Exports (USD billions) | Imports (USD billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 500 | 200 | 250 |
| 2021 | 550 | 220 | 270 |
| 2022 | 600 | 240 | 290 |
Anatolia’s Strategic Importance

Anatolia, the Asian part of Turkey, holds immense strategic significance due to its geographical location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. Throughout history, Anatolia has played a pivotal role in major conflicts and geopolitical events, serving as a gateway between continents and a battleground for empires.
Anatolia, a historical region in Western Asia, is home to diverse cultures and landscapes. From its bustling cities to its serene countryside, Anatolia offers a captivating experience. If you’re looking for a sun-soaked escape, consider exploring Alcudia on the island of Mallorca.
With its crystal-clear waters and pristine beaches, Alcudia offers a perfect respite from the hustle and bustle of everyday life. After soaking up the Mediterranean sun, return to Anatolia to delve into its rich history and cultural heritage.
Military Importance
Anatolia’s strategic location has made it a crucial military stronghold. The region’s rugged terrain and natural barriers, such as the Taurus and Pontic mountains, provide defensive advantages. Throughout history, Anatolia has been a staging ground for military campaigns, including the Persian-Greek wars, the Roman-Parthian wars, and the Ottoman-European conflicts.
Geopolitical Significance
Anatolia’s strategic location has also granted it geopolitical importance. The region serves as a bridge between the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea, and between the Middle East and Europe. This has made Anatolia a key transit point for trade and commerce, as well as a gateway for cultural and religious exchange.
Map of Anatolia Highlighting Its Strategic Location
The map below highlights the strategic location of Anatolia, situated at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.

Anatolia in the Modern World
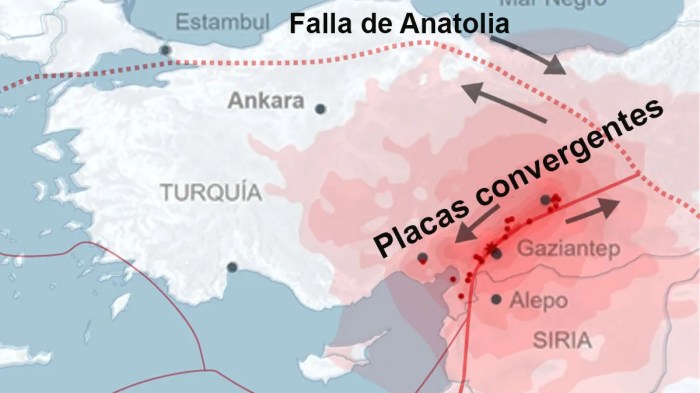
Anatolia, a land of rich history and strategic significance, continues to play a vital role in the modern world. As a crossroads of civilizations, Anatolia faces both challenges and opportunities, shaping its future trajectory.
Challenges
Anatolia faces several challenges in the modern world, including:
- Political Instability: Regional conflicts and geopolitical tensions can impact Anatolia’s stability and economic growth.
- Economic Disparities: Regional economic disparities persist, requiring balanced development and investment.
- Environmental Concerns: Urbanization, industrialization, and climate change pose environmental challenges that need sustainable solutions.
Opportunities
Despite these challenges, Anatolia presents significant opportunities for growth and development:
- Economic Potential: Anatolia’s strategic location, abundant resources, and skilled workforce offer potential for economic diversification and growth.
- Tourism and Heritage: Anatolia’s rich cultural heritage and historical sites attract tourists, contributing to economic development.
- Regional Cooperation: Anatolia’s role as a bridge between Europe and Asia provides opportunities for regional cooperation and economic integration.
Forecast for the Future
The future of Anatolia holds both promise and uncertainty. By addressing its challenges and capitalizing on its opportunities, Anatolia can continue to play a significant role in the modern world:
- Increased Economic Integration: Anatolia’s strategic location and economic potential can drive increased regional economic integration.
- Sustainable Development: Balanced development, environmental protection, and innovation will be crucial for Anatolia’s long-term prosperity.
- Enhanced Regional Cooperation: Anatolia’s role as a bridge between Europe and Asia will continue to facilitate regional cooperation and dialogue.
End of Discussion
As we delve into the depths of Anatolia’s captivating history, we uncover a land that has witnessed the rise and fall of civilizations, the clash of empires, and the birth of groundbreaking ideas. From the ancient ruins of Troy to the bustling streets of Istanbul, Anatolia’s rich tapestry of cultures and traditions continues to captivate and inspire.
Today, Anatolia stands as a vibrant and dynamic region, grappling with the challenges and embracing the opportunities of the 21st century. Its rich history and cultural heritage serve as a beacon of hope and resilience, reminding us of the enduring power of the human spirit.
Questions and Answers: Anatolia
What is the geographical significance of Anatolia?
Anatolia is a peninsula located at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, forming the westernmost part of Turkey. Its strategic location has made it a vital land bridge between the two continents, influencing trade, migration, and cultural exchange throughout history.
What are some of the major civilizations that have flourished in Anatolia?
Anatolia has been home to numerous civilizations over the millennia, including the Hittites, Phrygians, Lydians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Seljuks, and Ottomans. Each civilization has left its unique mark on the region, contributing to its rich cultural heritage.
What is Anatolia’s economic importance?
Anatolia has been an economically important region throughout history, due to its fertile land, abundant resources, and strategic location. Today, it is a major agricultural and industrial hub, contributing significantly to Turkey’s economy.